Boron nitride (BN) is a crystalline material composed of nitrogen and boron atoms and possesses four crystal structure variants: hexagonal, rhombic, cubic, and feldspar. Among them, hexagonal boron nitride (H-BN) and cubic boron nitride (C-BN) are two particularly important forms with very different properties. Hexagonal boron nitride is often referred to as “white graphene” because of its single-atom-layer, two-dimensional structure similar to graphene. Its atomic arrangement shows AA'AA' periodic layer stacking, and this structure gives it unique physicochemical properties. Hexagonal boron nitride is a lightweight white powder with a loose and porous microstructure, which is easy to adsorb water vapor on the surface, and has excellent high-temperature resistance, with experimental data showing that its thermal stability can be as high as 2800℃ or more. At room temperature, it is chemically inert to most metals, rare earth elements, glass and other substances, and is not easy to react. In addition, it has good insulation, oxidation resistance and mechanical strength. Based on these properties, hexagonal boron nitride shows broad application potential in the fields of composite material reinforcement, high-sensitivity sensor parts, field emission electron sources, deep-ultraviolet lasers, and high-temperature resistant protective coatings.
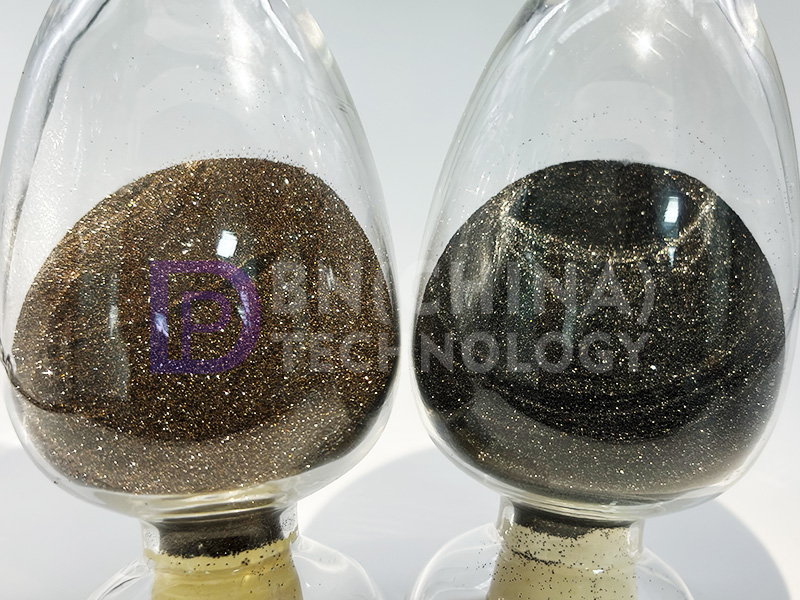
In contrast, cubic boron nitride is a synthetic superhard material with a Mohs hardness second only to diamond. It is usually prepared under high temperature and pressure using hexagonal boron nitride as a precursor and catalyzed by catalytic conversion. The appearance of cubic boron nitride is usually black, amber or with a sense of metal coating, and its particle size is generally less than 1 mm. It is not only highly thermally stable, but also exhibits excellent chemical inertness. It is these properties that make cubic boron nitride widely processed into super-hard cutting tools in industry, especially suitable for processing high hardness alloys and various wear-resistant materials. In summary, the core difference between the two boron nitride variants is very obvious: hexagonal boron nitride is a white powder and relatively soft texture, while cubic boron nitride has a dark appearance and very high hardness; in the direction of application, hexagonal boron nitride is mainly used as a basic material, can be used to further synthesize the cubic form, while the cubic boron nitride by virtue of its excellent mechanical properties, mainly as a core material for high-end cutting tools use. It is this significant difference in structure, performance and application that ultimately determines the unique technological positioning and industrial value of hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride in the field of materials science.




